This is a documentation for Board Game Arena: play board games online !
Scrollmap: Difference between revisions
Victoria La (talk | contribs) (added link to extensions) |
|||
| (28 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Studio_Framework_Navigation}} | |||
In some games, players are building the main game area with tiles or cards. Examples: | In some games, players are building the main game area with tiles or cards and it has no boundaries. | ||
This causes an additional difficulty for the adaptation, because we have to display an infinite game area into a finite space on the screen. | |||
This is where Scrollmap component can help you. | |||
Scrollmap is a BGA client side component to display an infinite game area. It supports Scrolling and Panning. | |||
Scrolling - allows user to scroll area inside the view port using the buttons drawn on the top/bottom/left/right. | |||
Panning - allows user to drag the surface area (using mouse). | |||
== Scrollmap in action == | |||
Examples of game that use Scrollmap (try on BGA or watch): | |||
* Carcassonne | * Carcassonne | ||
* Saboteur | * Saboteur | ||
* Takenoko | * Takenoko | ||
* Taluva | * Taluva | ||
In | In these games, you can see that there are arrow controls around the main game area, so that players can use them to scroll the view. You can also use Panning (i.e drag'n'drop the game area to scroll). | ||
== How to use Scrollmap == | == How to use Scrollmap == | ||
Open your template (TPL) file and add this HTML code: | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 46: | Line 30: | ||
<div id="map_surface"></div> | <div id="map_surface"></div> | ||
<div id="map_scrollable_oversurface"></div> | <div id="map_scrollable_oversurface"></div> | ||
< | |||
<div class="movetop"></div> | |||
<div class="movedown"></div> | |||
<div class="moveleft"></div> | |||
<div class="moveright"></div> | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
There are also some lines to add to your CSS stylesheet. Please note that you can adapt it to your needs, especially the default width of the scrollable area | There are also some lines to add to your CSS stylesheet. Please note that you can adapt it to your needs, especially the default width of the scrollable area. | ||
Do not change position and width/height of map_surface - it suppose to fill be exactly as container size. | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
/** Scrollable area **/ | /** Scrollable area **/ | ||
| Line 59: | Line 46: | ||
#map_container { | #map_container { | ||
position: relative; | position: relative; | ||
overflow: hidden; | |||
width: 100%; | width: 100%; | ||
height: 400px; | height: 400px; | ||
} | } | ||
#map_scrollable, #map_scrollable_oversurface { | #map_scrollable, #map_scrollable_oversurface { | ||
position: absolute; | position: absolute; | ||
} | } | ||
#map_surface { | #map_surface { | ||
| Line 76: | Line 62: | ||
cursor: move; | cursor: move; | ||
} | } | ||
/** This is some extra stuff to extend the container **/ | |||
#map_footer { | #map_footer { | ||
text-align: center; | text-align: center; | ||
} | } | ||
/** Move arrows **/ | |||
.movetop,.moveleft,.moveright,.movedown { | |||
display: block; | |||
position: absolute; | |||
background-image: url('../../../img/common/arrows.png'); | |||
width: 32px; | |||
height: 32px; | |||
} | |||
.movetop { | |||
top: 0px; | |||
left: 50%; | |||
background-position: 0px 32px; | |||
} | |||
.moveleft { | |||
top: 50%; | |||
left: 0px; | |||
background-position: 32px 0px; | |||
} | |||
.moveright { | |||
top: 50%; | |||
right: 0px; | |||
background-position: 0px 0px; | |||
} | |||
.movedown { | |||
bottom: 0px; | |||
left: 50%; | |||
background-position: 32px 32px; | |||
} | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Now in the Javascript file, add "ebg/scrollmap" as a dependency: | |||
<pre> | |||
define([ | |||
"dojo","dojo/_base/declare", | |||
"ebg/core/gamegui", | |||
"ebg/counter", | |||
"ebg/scrollmap" /// <==== HERE | |||
], | |||
</pre> | |||
Finally, to link your HTML code with your Javascript, place this in your Javascript "Setup" method: | Finally, to link your HTML code with your Javascript, place this in your Javascript "Setup" method: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
this.scrollmap = new ebg.scrollmap(); // declare an object (this can also go in constructor) | |||
// Make map scrollable | // Make map scrollable | ||
this.scrollmap.create( $('map_container'),$('map_scrollable'),$('map_surface'),$('map_scrollable_oversurface') ); | this.scrollmap.create( $('map_container'),$('map_scrollable'),$('map_surface'),$('map_scrollable_oversurface') ); // use ids from template | ||
this.scrollmap.setupOnScreenArrows( 150 ); | this.scrollmap.setupOnScreenArrows( 150 ); // this will hook buttons to onclick functions with 150px scroll step | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| Line 94: | Line 127: | ||
== Scrollable area layers == | == Scrollable area layers == | ||
There are | There are two and only two places where you should place your elements in your scrollable area: | ||
* inside "map_scrollable" div | * inside "map_scrollable" div | ||
* inside "map_scrollable_oversurface" div | * inside "map_scrollable_oversurface" div | ||
The difference is very important: "map_scrollable" is beneath the surface that is used to | The difference is very important: "map_scrollable" is beneath the surface that is used to pan scroll ("map_surface"), and "map_scrollable_oversurface" is above this surface. In practice: | ||
* If some element on the game area need to be clicked (or any kind of user interaction), you should place it in map_scrollable_oversurface, otherwise no click can reach it. | * If some element on the game area need to be clicked (or any kind of user interaction), you should place it in map_scrollable_oversurface, otherwise no click can reach it. | ||
* If some element on the game area don't need to be clicked, you'd better place it in "map_scrollable", so it is possible | * If some element on the game area don't need to be clicked, you'd better place it in "map_scrollable", so it is possible pan scroll from a point on this element. | ||
Of course, all layers are scrolled synchronously. | Of course, all layers are scrolled synchronously. | ||
| Line 106: | Line 139: | ||
Tips: in some situation, it's also useful to place a game element on map_scrollable and a corresponding invisible element over the surface to manage the interactions. Example: when an interactive element must be placed beneath a non interactive element for display reason. | Tips: in some situation, it's also useful to place a game element on map_scrollable and a corresponding invisible element over the surface to manage the interactions. Example: when an interactive element must be placed beneath a non interactive element for display reason. | ||
== | The other layer is 'map_surface' - it is what user would use to pan scroll. If this div is not visible because 'map_scrollable_oversurface' covering it completely - panning will be impossible (unless you apply some css trickery, see 'Fall-through mouse events on oversurface' below). | ||
By default, the game area (i.e. map_scrollable_oversurface) is centered on 0,0 coordinates. | |||
Simple example of placing element (normally you would use slideObject and such...): | |||
<pre> | |||
dojo.create("div",{innerHTML: "hello" },"map_scrollable_oversurface"); | |||
</pre> | |||
This is the layers of the scrollmap, it is not how it looks like, its just to visually demonstrate what is what: | |||
[[File:Scrollmap.png]] | |||
If you wondering on how to make this picture - I added transform: translateZ to layers to visually split them and removed visibily: hidden from the container to show that "map_scrollable" is the one that can grow without bounds and parts of it can be hidden because view port (the map_container) can be much smaller. Also you can see that map_scrollable_oversurface and map_scrollable are the layers that syncronized on position and size, | |||
and map_surface is same size as map_container. | |||
== Customizations == | |||
=== Disable move arrows === | |||
The buttons already defined in css and the buttons handler already defined in the scrollmap control just make sure you call function setupOnScreenArrows (and in .tpl file buttons have to be defined with exact these classes verbatim). If you don't want the buttons, do not call function setupOnScreenArrows() and remove them from template (you can also remove just some of them, i.e. only leave left and right). | |||
=== Enable scrollmap zone extension === | |||
This is optional, when there can be unused screen space under the scrollmap that a player might want to use. | |||
Add this in your .tpl after the scrollmap div (the matching css rules has already been defined): | |||
<pre> | |||
<div id="map_footer" class="whiteblock"> | |||
<a href="#" id="enlargedisplay">↓ {LABEL_ENLARGE_DISPLAY} ↓</a> | |||
</div> | |||
</pre> | |||
In your javascript, define the following function: | |||
<pre> | |||
onIncreaseDisplayHeight: function(evt) { | |||
console.log('Event: onIncreaseDisplayHeight'); | |||
evt.preventDefault(); | |||
var cur_h = toint(dojo.style( $('map_container'), 'height')); | |||
dojo.style($('map_container'), 'height', (cur_h + 300) + 'px'); | |||
}, | |||
</pre> | |||
and connect them to the 'enlargedisplay' link in your setup: | |||
<pre> | |||
dojo.connect( $('enlargedisplay'), 'onclick', this, 'onIncreaseDisplayHeight' ); | |||
</pre> | |||
In your view.php file, define the template variable LABEL_ENLARGE_DISPLAY so that it gets substituted with appropriate translatable text: | |||
<pre> | |||
$this->tpl['LABEL_ENLARGE_DISPLAY'] = self::_("Enlarge display"); | |||
</pre> | |||
=== Fall-through mouse events on oversurface === | |||
What if you have some non-square shapes on the surface and there is a lot of space in between the elemenets that can be | |||
used to pan scrolling but it currently not possible to grab on to map_scrollable_oversurface? | |||
To do that you have to make mouse click "fall-though" that layer, but stick on children. Add this to your css to solve this problem: | |||
<pre> | |||
#map_scrollable_oversurface { | |||
pointer-events: none; | |||
} | |||
#map_scrollable_oversurface > *{ | |||
pointer-events: initial; | |||
} | |||
</pre> | |||
=== Avoid scrolling on touch devices === | |||
When a scrollmap is used on touch devices (such as a smartphone), by default scrolling will scroll the entire page (and the elements in the scrollmap won't move). | |||
To avoid this, simply add the following in your CSS file: | |||
<pre> | |||
#map_container { | |||
touch-action: none; | |||
} | |||
</pre> | |||
=== Zooming === | |||
'''Ingredients:''' ggg_ggg.tpl, ggg.js | |||
Zooming elements on the scrollmap can be difficult because the different layers need to stay aligned (and there are many layers, due to BGA's zoom feature, screen resolution, ...) | |||
'''ggg_ggg.tpl''' | |||
Add 2 elements for zooming in and out | |||
<pre> | |||
<div id="zoomplus"></div> | |||
<div id="zoomminus"></div> | |||
</pre> | |||
'''ggg_ggg.js''' | |||
Bind it to a zoom function | |||
<pre> | |||
setup: function(gamedatas) { | |||
[...] | |||
this.trl_zoom = 1; | |||
dojo.connect($('zoomplus'), 'onclick', () => this.onZoomButton(0.1)); | |||
dojo.connect($('zoomminus'), 'onclick', () => this.onZoomButton(-0.1)); | |||
[...] | |||
}, | |||
onZoomButton: function(deltaZoom) { | |||
zoom = this.trl_zoom + deltaZoom; | |||
this.trl_zoom = zoom <= 0.2 ? 0.2 : zoom >= 2 ? 2 : zoom; | |||
dojo.style($('map_scrollable'), 'transform', 'scale(' + this.trl_zoom + ')'); | |||
dojo.style($('map_scrollable_oversurface'), 'transform', 'scale(' + this.trl_zoom + ')'); | |||
}, | |||
</pre> | |||
Note: you may also link this to a user preference (see [[Game_options_and_preferences:_gameoptions.inc.php#Updating_preference_from_code|this page]] for more information). | |||
=== Scrollmap Extensions === | |||
Its is possible to extend this class to add extra capabilities, for known forks see [[BGA Code Sharing]] | |||
== API Reference == | |||
=== Constructor === | |||
;ebg.scrollmap() | |||
:return newly created scrollmap object | |||
=== Properties === | |||
no public properties | |||
=== Methods === | |||
;create( container_div, undersurface_div, surface_div, onsurface_div ) | |||
:Object initializer, must be called before usage. | |||
:Parameters: | |||
::[HTMLElement] container_div - dom node of the container | |||
::[HTMLElement] undersurface_div - dom node of the layer under the scrollable surface, called map_scrollable in the template example | |||
::[HTMLElement] surface_div - dom node of the area inside the container that is used for panning | |||
::[HTMLElement] onsurface_div - dom node of the layer above the scrollable surface, called map_scrollable_oversurface in the template example | |||
:Note: this method also calles scrollto(0,0) which has animation, if you want to play with positioning you have to wait for it to finish (i.e. 350 ms for now). | |||
;scroll( dx, dy [, duration [, delay ]]) | |||
:Scroll content using relative offset (animated) | |||
:Parameters: | |||
::[Number] dx - x offset | |||
::[Number] dy - y offset | |||
::[Number] duration - animation duration, default is 350 | |||
::[Number] delay - animation duration, default is 0 | |||
;scrollto( x, y [, duration [, delay ]]) | |||
:Scroll the board to make it centered on given position (0,0 will scroll to center) | |||
:Parameters: | |||
::[Number] x - position relative to center | |||
::[Number] y - position relative to center | |||
::[Number] duration - animation duration, default is 350 | |||
::[Number] delay - animation duration, default is 0 | |||
;disableScrolling() | |||
:Disable scrolling (that disable both scrolling and panning) | |||
;enableScrolling() | |||
:Enable scrolling (re-enable scrolling) | |||
[[Category:Studio]] | |||
Revision as of 00:21, 24 January 2024
In some games, players are building the main game area with tiles or cards and it has no boundaries. This causes an additional difficulty for the adaptation, because we have to display an infinite game area into a finite space on the screen. This is where Scrollmap component can help you.
Scrollmap is a BGA client side component to display an infinite game area. It supports Scrolling and Panning. Scrolling - allows user to scroll area inside the view port using the buttons drawn on the top/bottom/left/right. Panning - allows user to drag the surface area (using mouse).
Scrollmap in action
Examples of game that use Scrollmap (try on BGA or watch):
- Carcassonne
- Saboteur
- Takenoko
- Taluva
In these games, you can see that there are arrow controls around the main game area, so that players can use them to scroll the view. You can also use Panning (i.e drag'n'drop the game area to scroll).
How to use Scrollmap
Open your template (TPL) file and add this HTML code:
<div id="map_container">
<div id="map_scrollable"></div>
<div id="map_surface"></div>
<div id="map_scrollable_oversurface"></div>
<div class="movetop"></div>
<div class="movedown"></div>
<div class="moveleft"></div>
<div class="moveright"></div>
</div>
There are also some lines to add to your CSS stylesheet. Please note that you can adapt it to your needs, especially the default width of the scrollable area. Do not change position and width/height of map_surface - it suppose to fill be exactly as container size.
/** Scrollable area **/
#map_container {
position: relative;
overflow: hidden;
width: 100%;
height: 400px;
}
#map_scrollable, #map_scrollable_oversurface {
position: absolute;
}
#map_surface {
position: absolute;
top: 0px;
left: 0px;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
cursor: move;
}
/** This is some extra stuff to extend the container **/
#map_footer {
text-align: center;
}
/** Move arrows **/
.movetop,.moveleft,.moveright,.movedown {
display: block;
position: absolute;
background-image: url('../../../img/common/arrows.png');
width: 32px;
height: 32px;
}
.movetop {
top: 0px;
left: 50%;
background-position: 0px 32px;
}
.moveleft {
top: 50%;
left: 0px;
background-position: 32px 0px;
}
.moveright {
top: 50%;
right: 0px;
background-position: 0px 0px;
}
.movedown {
bottom: 0px;
left: 50%;
background-position: 32px 32px;
}
Now in the Javascript file, add "ebg/scrollmap" as a dependency:
define([
"dojo","dojo/_base/declare",
"ebg/core/gamegui",
"ebg/counter",
"ebg/scrollmap" /// <==== HERE
],
Finally, to link your HTML code with your Javascript, place this in your Javascript "Setup" method:
this.scrollmap = new ebg.scrollmap(); // declare an object (this can also go in constructor)
// Make map scrollable
this.scrollmap.create( $('map_container'),$('map_scrollable'),$('map_surface'),$('map_scrollable_oversurface') ); // use ids from template
this.scrollmap.setupOnScreenArrows( 150 ); // this will hook buttons to onclick functions with 150px scroll step
This is it! Now, you should see on your game interface a scrollable game area. This is not really impressive though, because you didn't add anything on the game area yet. This is the next step.
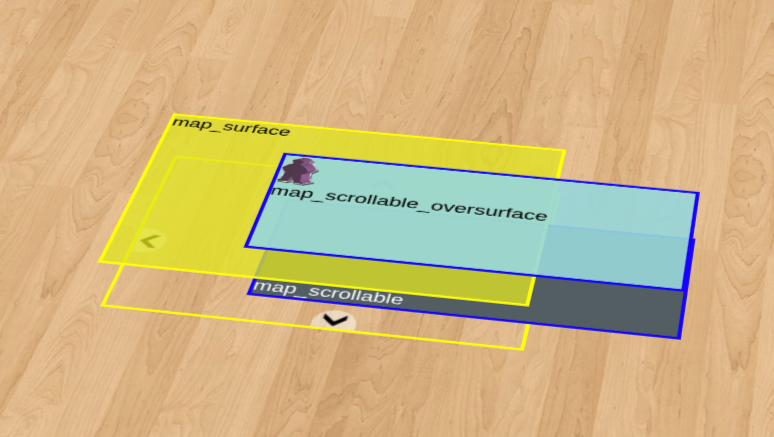
Scrollable area layers
There are two and only two places where you should place your elements in your scrollable area:
- inside "map_scrollable" div
- inside "map_scrollable_oversurface" div
The difference is very important: "map_scrollable" is beneath the surface that is used to pan scroll ("map_surface"), and "map_scrollable_oversurface" is above this surface. In practice:
- If some element on the game area need to be clicked (or any kind of user interaction), you should place it in map_scrollable_oversurface, otherwise no click can reach it.
- If some element on the game area don't need to be clicked, you'd better place it in "map_scrollable", so it is possible pan scroll from a point on this element.
Of course, all layers are scrolled synchronously.
Tips: in some situation, it's also useful to place a game element on map_scrollable and a corresponding invisible element over the surface to manage the interactions. Example: when an interactive element must be placed beneath a non interactive element for display reason.
The other layer is 'map_surface' - it is what user would use to pan scroll. If this div is not visible because 'map_scrollable_oversurface' covering it completely - panning will be impossible (unless you apply some css trickery, see 'Fall-through mouse events on oversurface' below).
By default, the game area (i.e. map_scrollable_oversurface) is centered on 0,0 coordinates.
Simple example of placing element (normally you would use slideObject and such...):
dojo.create("div",{innerHTML: "hello" },"map_scrollable_oversurface");
This is the layers of the scrollmap, it is not how it looks like, its just to visually demonstrate what is what:
If you wondering on how to make this picture - I added transform: translateZ to layers to visually split them and removed visibily: hidden from the container to show that "map_scrollable" is the one that can grow without bounds and parts of it can be hidden because view port (the map_container) can be much smaller. Also you can see that map_scrollable_oversurface and map_scrollable are the layers that syncronized on position and size, and map_surface is same size as map_container.
Customizations
Disable move arrows
The buttons already defined in css and the buttons handler already defined in the scrollmap control just make sure you call function setupOnScreenArrows (and in .tpl file buttons have to be defined with exact these classes verbatim). If you don't want the buttons, do not call function setupOnScreenArrows() and remove them from template (you can also remove just some of them, i.e. only leave left and right).
Enable scrollmap zone extension
This is optional, when there can be unused screen space under the scrollmap that a player might want to use. Add this in your .tpl after the scrollmap div (the matching css rules has already been defined):
<div id="map_footer" class="whiteblock">
<a href="#" id="enlargedisplay">↓ {LABEL_ENLARGE_DISPLAY} ↓</a>
</div>
In your javascript, define the following function:
onIncreaseDisplayHeight: function(evt) {
console.log('Event: onIncreaseDisplayHeight');
evt.preventDefault();
var cur_h = toint(dojo.style( $('map_container'), 'height'));
dojo.style($('map_container'), 'height', (cur_h + 300) + 'px');
},
and connect them to the 'enlargedisplay' link in your setup:
dojo.connect( $('enlargedisplay'), 'onclick', this, 'onIncreaseDisplayHeight' );
In your view.php file, define the template variable LABEL_ENLARGE_DISPLAY so that it gets substituted with appropriate translatable text:
$this->tpl['LABEL_ENLARGE_DISPLAY'] = self::_("Enlarge display");
Fall-through mouse events on oversurface
What if you have some non-square shapes on the surface and there is a lot of space in between the elemenets that can be used to pan scrolling but it currently not possible to grab on to map_scrollable_oversurface? To do that you have to make mouse click "fall-though" that layer, but stick on children. Add this to your css to solve this problem:
#map_scrollable_oversurface {
pointer-events: none;
}
#map_scrollable_oversurface > *{
pointer-events: initial;
}
Avoid scrolling on touch devices
When a scrollmap is used on touch devices (such as a smartphone), by default scrolling will scroll the entire page (and the elements in the scrollmap won't move). To avoid this, simply add the following in your CSS file:
#map_container {
touch-action: none;
}
Zooming
Ingredients: ggg_ggg.tpl, ggg.js
Zooming elements on the scrollmap can be difficult because the different layers need to stay aligned (and there are many layers, due to BGA's zoom feature, screen resolution, ...)
ggg_ggg.tpl
Add 2 elements for zooming in and out
<div id="zoomplus"></div>
<div id="zoomminus"></div>
ggg_ggg.js
Bind it to a zoom function
setup: function(gamedatas) {
[...]
this.trl_zoom = 1;
dojo.connect($('zoomplus'), 'onclick', () => this.onZoomButton(0.1));
dojo.connect($('zoomminus'), 'onclick', () => this.onZoomButton(-0.1));
[...]
},
onZoomButton: function(deltaZoom) {
zoom = this.trl_zoom + deltaZoom;
this.trl_zoom = zoom <= 0.2 ? 0.2 : zoom >= 2 ? 2 : zoom;
dojo.style($('map_scrollable'), 'transform', 'scale(' + this.trl_zoom + ')');
dojo.style($('map_scrollable_oversurface'), 'transform', 'scale(' + this.trl_zoom + ')');
},
Note: you may also link this to a user preference (see this page for more information).
Scrollmap Extensions
Its is possible to extend this class to add extra capabilities, for known forks see BGA Code Sharing
API Reference
Constructor
- ebg.scrollmap()
- return newly created scrollmap object
Properties
no public properties
Methods
- create( container_div, undersurface_div, surface_div, onsurface_div )
- Object initializer, must be called before usage.
- Parameters:
- [HTMLElement] container_div - dom node of the container
- [HTMLElement] undersurface_div - dom node of the layer under the scrollable surface, called map_scrollable in the template example
- [HTMLElement] surface_div - dom node of the area inside the container that is used for panning
- [HTMLElement] onsurface_div - dom node of the layer above the scrollable surface, called map_scrollable_oversurface in the template example
- Note: this method also calles scrollto(0,0) which has animation, if you want to play with positioning you have to wait for it to finish (i.e. 350 ms for now).
- scroll( dx, dy [, duration [, delay ]])
- Scroll content using relative offset (animated)
- Parameters:
- [Number] dx - x offset
- [Number] dy - y offset
- [Number] duration - animation duration, default is 350
- [Number] delay - animation duration, default is 0
- scrollto( x, y [, duration [, delay ]])
- Scroll the board to make it centered on given position (0,0 will scroll to center)
- Parameters:
- [Number] x - position relative to center
- [Number] y - position relative to center
- [Number] duration - animation duration, default is 350
- [Number] delay - animation duration, default is 0
- disableScrolling()
- Disable scrolling (that disable both scrolling and panning)
- enableScrolling()
- Enable scrolling (re-enable scrolling)